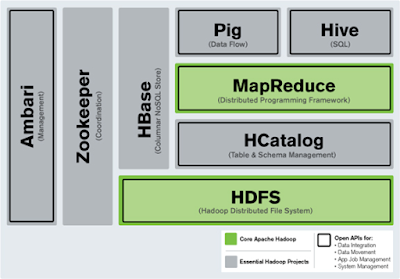
HDFS vs. HBase : All you need to know
The sudden increase in the volume of data from the order of
gigabytes to zettabytes has created the need for a more organized file system
for storage and processing of data. The demand stemming from the data market
has brought Hadoop in the limelight
making it one of biggest players in the industry. Hadoop Distributed File
System (HDFS), the commonly known file system of Hadoop and Hbase (Hadoop’s
database) are the most topical and advanced data storage and management systems
available in the market.
What are HDFS and HBase?
HDFS is fault-tolerant by design and supports rapid data
transfer between nodes even during system failures. HBase is a non-relational
and open source Not-Only-SQL database that runs on top of Hadoop. HBase comes
under CP type of CAP (Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance)
theorem.
HDFS is most suitable for performing batch analytics. However,
one of its biggest drawbacks is its inability to perform real-time analysis,
the trending requirement of the IT industry. HBase, on the other hand, can
handle large data sets and is not appropriate for batch analytics. Instead, it
is used to write/read data from Hadoop in real-time.
Both HDFS and HBase are capable of processing structured,
semi-structured as well as un-structured data. HDFS lacks an in-memory
processing engine slowing down the process of data analysis; as it is using
plain old MapReduce to do it. HBase, on the contrary, boasts of an in-memory
processing engine that drastically increases the speed of read/write.
HDFS is very transparent in its execution of data
analysis. HBase, on the other hand, being a NoSQL database in tabular
format, fetches values by sorting them under different key values.
Enhanced Understanding
with Use Cases for HDFS & HBase
Use Case 1 – Cloudera optimization
for European bank using HBase
HBase is ideally suited for real-time environments and this can
be best demonstrated by citing the example of our client, a renowned European
bank. To derive critical insights from the logs from application/web servers,
we implemented solution in Apache Storm and Apache Hbase together. Given the
huge velocity of data, we opted for HBase over HDFS; as HDFS does not support
real-time writes. The results were overwhelming; it reduced the query time from
3 days to 3 minutes.
Use Case 2 – Analytics
solution for global CPG player using HDFS & MapReduce
With our global beverage player client, the primary objective
was to perform batch analytics to gain SKU level insights, and involved
recursive/sequential calculations. HDFS and MapReduce frameworks were better
suited than complex Hive queries on top of Hbase. MapReduce was used for data
wrangling and to prepare data for subsequent analytics. Hive was used for
custom analytics on top of data processed by MapReduce. The results were
impressive; as there was a drastic reduction in the time taken to generate
custom analytics – 3 days to 3 hours.
To
offer a reasonable comparison between HDFS and HBase, the following points need
to be emphasized on:
|
HDFS
|
HBase
|
|
HDFS
is a Java-based file system utilized for storing large data sets.
|
HBase
is a Java based Not Only SQL database
|
|
HDFS
has a rigid architecture that does not allow changes. It doesn’t facilitate
dynamic storage.
|
HBase
allows for dynamic changes and can be utilized for standalone applications.
|
|
HDFS
is ideally suited for write-once and read-many times use cases
|
HBase
is ideally suited for random write and read of data that is stored in HDFS.
|


Comments
Post a Comment